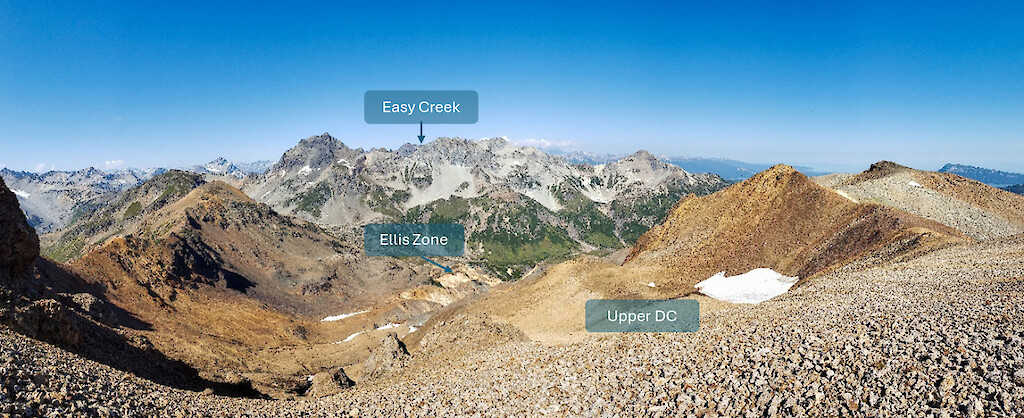
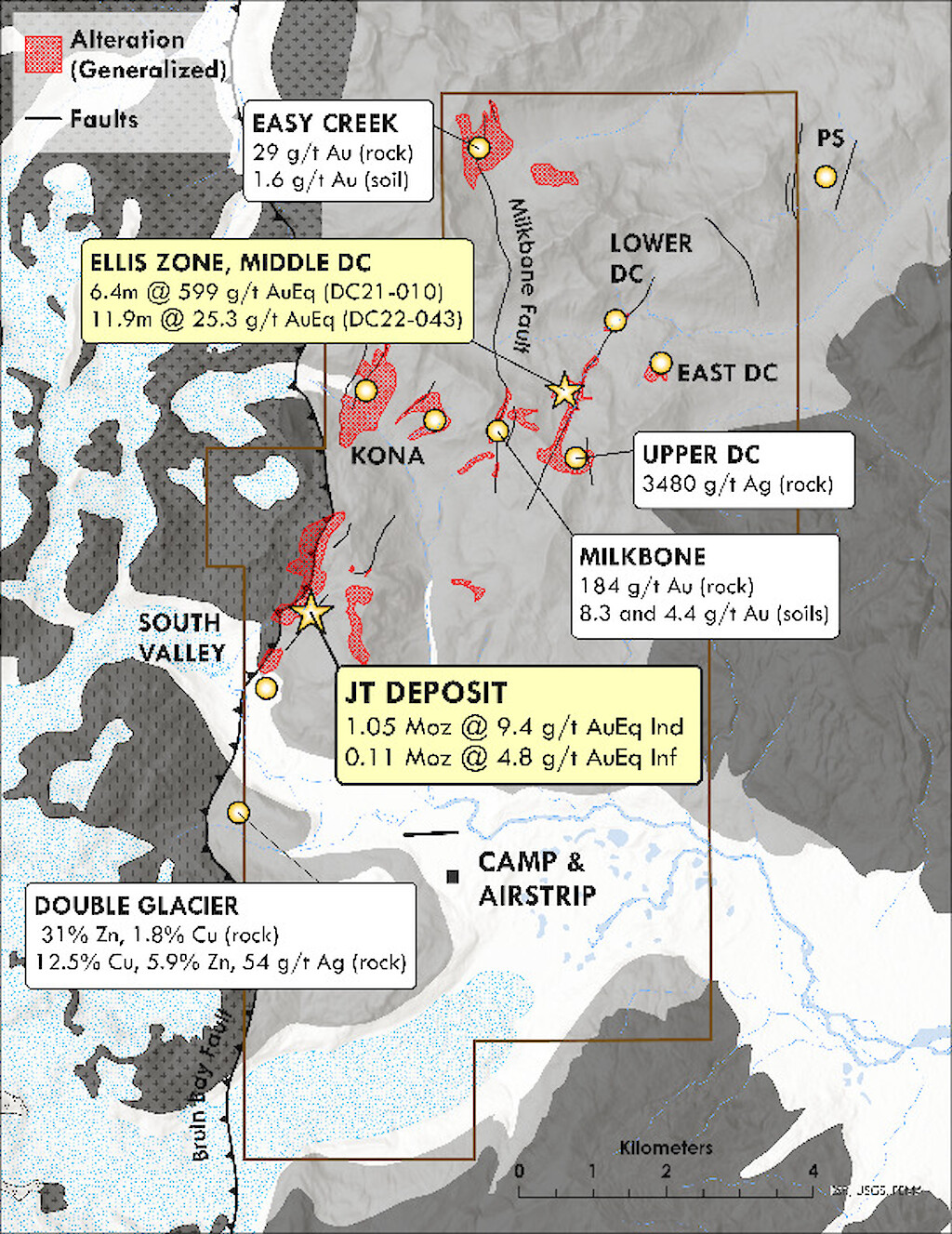
The DC Prospect is located four (4) kilometers northeast of the JT Deposit and is characterized by a series of large gossan alteration zones that extends over a 1.5 km x 3.0 km area, focused along a northeast-striking structure, similar to the JT Deposit. Mineralization and pervasive clay/anhydrite alteration are preferentially developed within dacitic volcaniclastic rocks capped by a shallowly dipping sequence of lesser altered basaltic volcanic rocks that are host to a gold- and silver-rich epithermal vein field at higher elevations. The widespread extent of alteration and mineralization exposed in erosional windows through the capping basalt supports potential for a large and partially blind mineralized system linking the various DC Prospect zones together over a strike length of 3 km.
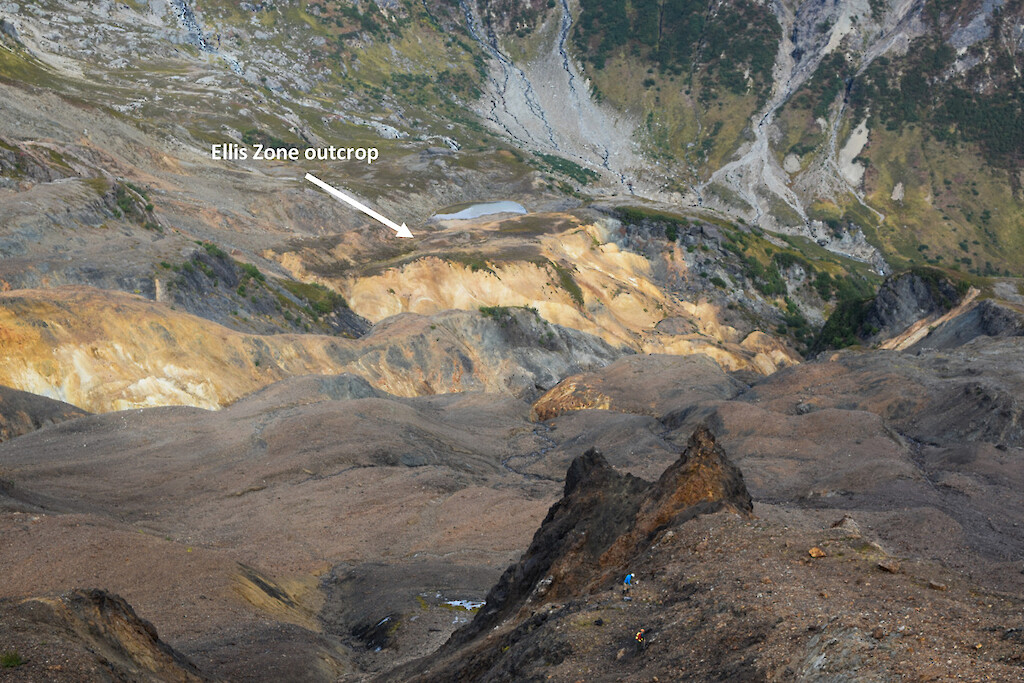
Drilling in 2021 resulted in the discovery of the “Ellis Zone” as near-surface bonanza-grade mineralization, which returned 577.9 g/t Au and 2,023 g/t Ag over 6.40 m in hole DC21-010. The Ellis Zone was expanded in 2022 and 2023, and mineralization has now been defined over a strike length of 125 meters and from surface to a depth of 225 meters with an average true thickness of 10 to 15m within the plunging core of the zone. Other significant intercepts include:
- 14.3 g/t AuEq over 14.8 m (DC22-046),
- 21.7 g/t AuEq over 11.9 m (DC22-043), and
- 5.4 g/t AuEq over 42.8 m (DC22-046).
The Ellis Zone shares many similarities with the JT Deposit, including high base and precious metal grades, steep geometry, coarse-grained base metal sulfides in stockwork veins and siliceous breccia, within anhydrite-altered dacitic fragment rocks. Anhydrite-chlorite alteration is zoned outboard to a widespread zone of pyrite-sericite (± clay) alteration.
The Ellis Zone remains open along trend and at depth. TravisGold Global continues to grow the Ellis Zone with the objective of generating a resource estimate for the new discovery, while also testing the greater potential at the DC prospect.
Property Map
View looking North from Upper DC towards the Ellis Zone at Middle DC. Vein sampling at Upper DC for scale.

Ellis Zone Cross-Section


